
Your Guide to Creative 3D Print Projects
What if you could hold an idea in your hand just moments after thinking it up? That’s not science fiction anymore. It’s the incredible reality of 3D printing, a technology that breathes life into your digital visions. Forget massive, complex factories; this is about having a personal tool for creation right at your fingertips.
Turn Your Digital Dreams Into Physical Reality
At its core, 3D printing is a straightforward process: it builds an object one whisper-thin layer at a time from a digital blueprint. Imagine it like building with digital LEGOs, but with incredible precision.
Instead of starting with a block of material and carving away what you don't need (subtractive manufacturing), a 3D printer does the opposite. It adds material only where it’s needed. This is why it's called additive manufacturing.
This clever approach sidesteps many traditional manufacturing hurdles. It empowers you to bring an idea to life without needing costly molds or a complicated supply chain. The journey from a spark of inspiration to a finished object is surprisingly direct.
The Creative Workflow From Idea to Object
The entire process boils down to three actionable stages, each bringing you one step closer to holding your creation:
- Design: Start with a 3D model. You can either design your own from scratch using free or professional software like Tinkercad or Fusion 360, or download millions of ready-to-print designs from online communities like Thingiverse or Printables.
- Slice: Next, use a "slicer" program (like Cura or PrusaSlicer) to translate your 3D model. It slices the model into hundreds of thin horizontal layers and generates a G-code file—the step-by-step instruction manual for your printer.
- Print: Finally, load the G-code file onto your printer. It reads the instructions and meticulously builds your object, one layer on top of the next, until the final piece emerges.
This infographic gives you a great visual of how a simple digital file is methodically built up into a solid, physical object.
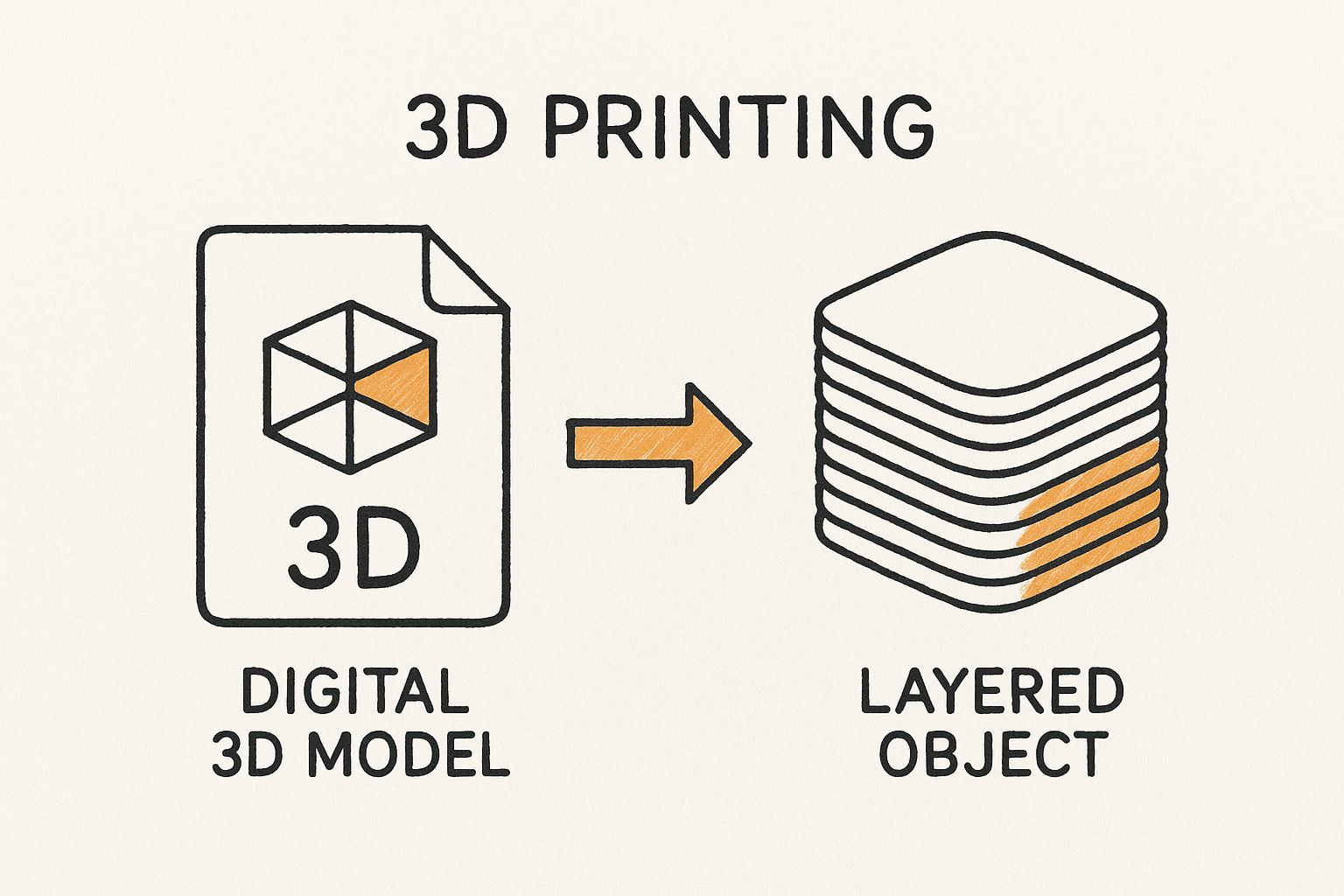
It’s this simple yet powerful layer-by-layer method that makes 3D printing so incredibly versatile.
The Growing Impact of Additive Manufacturing
The accessibility and potential of this technology have sparked a fire. The global 3D printing market was already valued at USD 15.39 billion in 2024 and is expected to more than double to USD 35.79 billion by 2030. This boom is being fueled by better, faster machines and a growing hunger for personalized products across healthcare, cars, and even the things we buy every day. You can discover more insights about the 3D printing market growth and see just how big this is getting.
This isn't just a niche hobby; it's a fundamental shift in how we think about production. It democratizes manufacturing, placing the power to create directly into the hands of individuals and small businesses.
What was once the exclusive domain of high-tech labs and giant factories can now sit on your desktop. This opens up a universe of possibilities for creating custom solutions, unique art, and functional items designed to fit your life perfectly. The only real limit is your own imagination.
Choosing the Right 3D Print Technology
Stepping into the world of 3D printing is like walking into a workshop filled with specialized tools. While they all serve to bring ideas to life, each one has unique strengths.
Not all 3D printing methods are created equal. The secret to a stunning final piece lies in choosing the right process from the start. Are you making a sturdy, functional part? Or a delicate sculpture with intricate details? Let's break down the most popular technologies to find the perfect fit for your vision.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): The Precise Glue Gun
Imagine a tiny, incredibly precise robotic hot glue gun, and you've basically got Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). This is the most common technology for hobbyists and for good reason—it’s a reliable and straightforward workhorse.
An FDM printer works by feeding a spool of plastic filament into a heated nozzle, melting it, and then carefully drawing out your object one layer at a time. This method excels at creating strong, durable parts, making it perfect for rapid prototypes, custom-fit brackets, phone stands, or just about any functional item where toughness matters most.
Stereolithography (SLA): Drawing with Light
Now, let's get a little more magical. What if you could literally draw an object into existence with a beam of light? That's the essence of Stereolithography (SLA). Instead of melting plastic, an SLA printer uses a highly-focused ultraviolet (UV) laser to cure liquid resin in a vat, solidifying it layer by delicate layer.
The result is an astonishing level of detail. Use SLA for projects where a flawless, smooth surface and intricate features are non-negotiable—think detailed miniatures, custom jewelry, or precise dental models. The trade-off is that these beautiful parts aren't quite as tough as their FDM cousins, but when it comes to visual perfection, SLA is in a class of its own.
Choosing a 3D print technology is less about which one is "best" and more about which one best serves your creative purpose. A technology that’s perfect for an engineer's prototype might be the wrong choice for an artist's sculpture.
To help you get a clearer picture, it’s useful to see these technologies side-by-side.
Comparing Popular 3D Printing Technologies
This table breaks down the core differences, giving you a quick guide to match your project's needs with the right process.
| Technology | How It Works | Best For | Common Materials | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FDM | Melts and extrudes plastic filament layer by layer. | Functional prototypes, large models, and durable parts. | PLA, PETG, ABS | Strength and Cost |
| SLA | Cures liquid resin with a UV laser. | High-detail models, jewelry, and smooth miniatures. | Standard & Specialty Resins | Fine Detail & Smooth Finish |
| SLS | Fuses nylon powder together with a high-power laser. | Complex geometries, interlocking parts, and durable end-use products. | Nylon Powders | Design Freedom & Durability |
Each method offers a distinct set of superpowers, from the brute strength of FDM to the surgical precision of SLA and the incredible freedom of SLS.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): Building with Powder
Last but not least, we have Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), which plays by a completely different set of rules. Picture a shallow bed filled with a fine polymer powder. A powerful laser dances across the surface, fusing particles together to create a solid cross-section of your design. The bed then lowers, a fresh layer of powder is spread on top, and the laser goes to work again.
Here’s the genius part: the loose, unfused powder acts as a natural support for the object as it prints. This unlocks total design freedom. You can create incredibly complex geometries, moving parts, and interlocking pieces straight off the printer—things that would be impossible with other methods. SLS produces strong, functional nylon parts ready for real-world use, making it a favorite for professional engineers and small-batch manufacturers.
Choosing Your Palette of Creative Materials

The material you choose for your 3D print is just as important as the design itself. It's the substance that brings a digital blueprint into the physical world, giving it texture, weight, and character. Think of it less like a technical choice and more like an artist selecting from a palette of plastics, resins, and composites.
Don't get bogged down in complex chemical names. The key is to think about what you want to make. This guide will introduce you to the most popular and inspiring options, helping you understand their unique properties so you can bring your vision to life.
The Go-To Materials for Everyday Creating
For most of your projects, a few trusty materials will get the job done beautifully. These are the reliable workhorses of the 3D printing world, loved for being easy to work with and delivering great results. Start with these to build your confidence and skills.
-
PLA (Polylactic Acid): This is the undisputed champion for anyone new to 3D printing. PLA is a bioplastic, often made from corn starch, and it’s incredibly forgiving. It prints with sharp details and a smooth finish with almost no fuss, making it perfect for decorative objects, prototypes, and anything that won't be exposed to high heat or serious stress.
-
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): When you need more muscle than PLA can offer, use PETG. It’s in the same plastic family as water bottles, so it has a fantastic balance of strength, heat resistance, and a touch of flexibility. This makes it ideal for functional parts like phone cases, small brackets, or anything that needs to stand up to daily life.
Elevating Your Prints with Specialty Materials
Once you've mastered the basics, a whole new world of creativity opens up. Specialty filaments are engineered to mimic the look and feel of other materials, letting you create objects with stunning aesthetics that go far beyond simple plastic.
They can transform a standard 3D print into something that feels premium, organic, or wonderfully tactile. While they might require more fine-tuning in your slicer settings, the incredible results are more than worth it.
Choosing a specialty material is a declaration of intent. It's deciding that your object should not only be functional but also tell a story through its very texture and appearance, connecting the digital process with the physical world in a more profound way.
You can craft truly unique pieces that blend seamlessly into your home’s aesthetic. For a little inspiration, see how different materials can be used to create stunning minimalist decor in our guide to the 3D print vase.
Ready to experiment? Here are a few amazing options to consider:
-
Wood-Fill Filaments: These are a beautiful composite of plastic (usually PLA) mixed with fine wood particles. The finished prints look and feel genuinely organic. You can even sand and stain them just like real wood, making them perfect for creating decor with a warm, natural vibe.
-
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): If you need something soft and flexible, TPU is your material. It prints into rubber-like objects that can bend, stretch, and absorb shock. Think of things like custom phone cases, flexible joints, or comfortable grips for tools.
-
Metal-Infused Filaments: These amazing filaments blend fine metal powders—like bronze, copper, or stainless steel—into a plastic base. The printed parts have a surprising weight and a beautiful metallic sheen. After printing, you can polish them to a brilliant shine, giving them the impressive look and feel of solid cast metal.
Designing for a Purposeful Modern Home
A 3D printer isn't just a gadget; it's your personal gateway to crafting a home that feels uniquely yours. It’s about moving past mass-produced items and filling your space with objects that are not only beautiful but also perfectly suited to your life. This is where modern design—with its clean lines and clutter-free spirit—truly comes alive through the magic of a 3d print.
The real power here is the ability to solve your own everyday problems with elegance. Think about those little frustrations around your home: the nest of tangled cables behind the TV, that one chaotic drawer where everything gets lost, or the awkward, empty corner that just needs something. With a 3D printer, you become the problem-solver, creating bespoke solutions that blend right into your home's aesthetic.
You're no longer just a consumer; you're a creator. Every object you make has a story, a purpose, and a place, designed with intention, by you and for you.
Minimalist Project Ideas You Can Start Today
Minimalism isn't about deprivation; it's about surrounding yourself with things that are essential, functional, and bring you joy. A 3D printer is the perfect tool for this philosophy, empowering you to create items that nail both form and function.
Ready for some inspiration? Here are a few actionable ideas to get your creative gears turning:
- Custom-Fit Drawer Organizers: Don't buy another flimsy plastic tray. Measure your drawer's exact dimensions and design dividers in Tinkercad that fit perfectly, turning chaos into a beautifully organized space.
- Sleek Wall-Mounted Planters: Bring greenery into your home without sacrificing floor space. Design minimalist planters with integrated mounting holes that seem to float on your walls. You can shape them to match your decor perfectly.
- Bespoke Cable Management Solutions: Finally tame that "cable spaghetti." Print custom clips, hubs, and channels that guide wires neatly along walls or under desks. Search for "cable management" on Printables.com for thousands of ready-to-print solutions.
These projects don't just organize; they embody the idea that good design serves a purpose. To see how these ideas come to life, explore this fantastic collection of 3D printed home decor that can elevate any modern home.
Designing Smarter, Not Harder
Bringing a beautiful object to life is one thing. But to truly master designing for a 3d print, you have to start thinking like the printer thinks. Making smart choices in your design can save you time, material, and a lot of headaches, resulting in stronger, cleaner final products.
The most elegant designs are often the ones that work in harmony with the tool that creates them. By understanding the nature of 3D printing, you can create objects that are not only visually appealing but also intelligently engineered for the process.
This means thinking in layers from the very beginning. How will the printer build this shape? Where might a weak point emerge? Even tiny adjustments in your digital model can make a world of difference.
Key Considerations for Flawless Prints
Optimizing your designs is a creative puzzle, and solving it is incredibly satisfying. Keep these principles in mind, and you'll be well on your way to a successful print, every single time.
-
Optimize for Strength: An object’s durability often comes down to its orientation on the print bed. Always try to orient your model so that pulling forces (tensile stress) run along the printed layers, not against them where they can easily split. This simple step can make a part up to 3 times stronger.
-
Reduce Material Usage: You can design incredibly strong yet lightweight parts by focusing on the outer walls (perimeters) instead of the filling (infill). Most of an object's strength comes from its shell. Increasing the number of perimeters in your slicer is a much more efficient way to add strength than just cranking up the infill percentage.
-
Design for Support-Free Printing: Support structures are like temporary scaffolding—they use extra material and time, and you just throw them away. By designing with overhangs of less than 45 degrees and using clever tricks like chamfers instead of sharp curves, you can often print without any supports at all. This saves plastic, cuts down on print time, and leaves you with a much cleaner finish straight off the printer.
Embracing a Smarter, More Sustainable Way to Create
There’s a kind of magic to watching a 3D printer at work, but the real wonder isn’t just in the beautiful objects it creates. It's in the profound shift it represents—a move toward a more conscious and sustainable way of making things. This technology challenges us to think differently not just about what we make, but how we make it. It’s an open invitation to step away from the wasteful, one-size-fits-all model of mass production and into a future where we create exactly what we need, when and where we need it.
At its core, 3D printing is an additive process. It adds material one layer at a time until the final shape emerges. Only the material needed for the object is used.
This is a world away from traditional subtractive manufacturing, which is more like carving a sculpture from a block of marble. You start with a big chunk of material and chip away everything you don't need, leaving piles of waste behind. By building up instead of cutting down, 3D printing can slash material waste by up to 90% on complex designs. This on-demand approach also means no more warehouses overflowing with unsold products—we simply print what’s required, using our planet's resources with intention and care.
Shrinking the World, One Local Print at a Time
Beyond saving materials, 3D printing holds the key to dramatically reducing our collective carbon footprint. Think about the journey of a typical mass-produced item: raw materials are mined, shipped to be processed, sent to another factory for assembly, and finally trucked and flown all over the world for sale. Every step leaves a long, polluting trail.
3D printing flips that entire model on its head.
With the power of local, on-demand production, your desk or studio effectively becomes a micro-factory. The vast, carbon-heavy distance between an idea and a finished object collapses, sidestepping the complex logistics that define global commerce.
This is a game-changer. Suddenly, we can produce goods right where they're needed. A broken part for a kitchen appliance or a custom-designed piece of furniture can be printed locally, completely eliminating the environmental toll of international shipping. It’s a powerful step toward a more resilient, self-sufficient, and localized economy.
Crafting with a Conscience: The Rise of Eco-Friendly Materials
The sustainability narrative gets even better when you look at the materials themselves. The 3D printing world is humming with innovation, giving us an ever-expanding menu of eco-friendly filaments that let us create with a truly clear conscience.
These aren't just niche experiments; they are beautiful, high-performance materials making sustainable design more accessible than ever. Here are some of the most exciting options available today:
- Plant-Based Bioplastics: PLA is the undisputed star here. Made from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane, it’s biodegradable in industrial composting facilities, making it a far kinder choice than traditional petroleum-based plastics.
- Recycled Filaments: Visionary makers are transforming our trash into treasure. Plastic waste, from single-use water bottles (rPETG) to discarded manufacturing scraps, is being repurposed into top-quality filaments. This circular economy approach breathes new life into old materials and lessens our dependence on creating new plastic from scratch.
By choosing these materials, every object you create becomes more than just a beautiful piece—it becomes part of a bigger solution. If you’re looking for more ways to bring this mindset into your living space, explore our guide on eco-friendly home accents. By pairing smarter materials with a more intelligent production process, every single 3D print becomes a small but vital step toward a more responsible and sustainable future for all of us.
How 3D Printing Is Building Our World
https://www.youtube.com/embed/vL2KoMNzGTo
The same ideas that bring a small creation to life on your desk are now being used on a scale that’s hard to wrap your head around. It’s a moment where the quiet hum of a home workshop grows into the roar of global innovation, literally building the world we live in. What starts as a simple layered object in your home is now laying the foundation for our future.
Picture a giant robotic arm, but instead of a tiny nozzle melting plastic, it’s extruding layers of specialized concrete. This is the incredible world of 3D printed construction, a powerful evolution of the technology that’s set to build homes, shelters, and even entire communities faster and more affordably than ever before. Better yet, it does all this with a fraction of the waste.
This isn't some far-off sci-fi dream. It's happening right now, reshaping how we think about building and design. This technology gives architects the freedom to create complex, curved walls and beautiful features that would be astronomically expensive or even impossible with old-school methods.
From Blueprints to Buildings
The process is surprisingly familiar, just on a massive scale. An architect’s digital model is sliced into layers, and a colossal gantry-style printer follows that blueprint, methodically building the walls up one layer at a time.
The advantages are game-changing, especially when you think about some of the world’s most pressing problems.
- Speed: A basic house frame, which might normally take weeks to build, can be printed in as little as 24 hours.
- Cost Reduction: Automating much of the labor and using materials so precisely slashes construction costs, a huge step toward making housing more accessible for everyone.
- Sustainability: Concrete is printed only where it’s needed. This cuts down on the tons of waste that traditional construction sites send to landfills.
This is about more than just building houses; it's about building hope. For communities hit by natural disasters or those struggling with housing shortages, 3D printing offers a way to provide safe, dignified shelter almost immediately.
A Market on the Rise
The potential here is staggering, and the numbers show it. The 3D printing construction market was valued at about USD 53.9 million in 2024, but it’s projected to explode to USD 4.18 billion by 2030. This incredible growth is fueled by large-scale building projects and the rise of smart city initiatives. You can read the full research about construction market growth to truly grasp the scale of this shift.
This technology connects the accessible tool on your desk to the global innovations solving some of our biggest challenges. It's a powerful reminder that every layer, no matter how small, contributes to building a better, smarter, and more sustainable world.
The simple act of creating something in your own home is part of a much bigger story—a story of innovation, compassion, and progress, written one layer at a time.
Answering Your Top 3D Printing Questions
Stepping into the world of 3D printing is an amazing adventure, but it's normal to have questions. Think of these as stepping stones, not stumbling blocks—each one you answer builds your confidence and brings you closer to creating incredible things.
Let's clear up some of the most common questions and give you actionable solutions.
What’s the Best 3D Printer for a Beginner?
This is the big one. The best printer for a beginner isn't the most expensive or complicated one. It’s the one that lets you start making things, not just tinkering with the machine itself.
Actionable Tip: When you're starting out, prioritize printers with features like auto-bed leveling, a strong user community, and good customer support. These features save you from common frustrations and help you get a successful first print quickly, which is key to staying motivated. Popular entry-level brands like Creality, Elegoo, or Bambu Lab are great places to start your research.
The best tool isn’t the one with the most bells and whistles. It's the one that gets out of your way and lets you create. A simple, reliable machine that works from day one is your biggest ally.
How Do I Fix Common Print Problems?
So, you’ve got your printer, but your first few attempts aren't perfect. Welcome to the club! Every single person who 3D prints has been there. Learning to troubleshoot is part of the craft, and it’s incredibly rewarding when you solve a problem.
Most early issues are surprisingly easy to fix. Here are two of the most common hurdles and how to clear them:
-
Problem: My Print Won't Stick! (Bed Adhesion):
- Quick Fix: Clean your print bed thoroughly with isopropyl alcohol to remove any fingerprints or dust.
- Next Step: Make sure your first layer is printing correctly. In your slicer, slightly slow down the print speed for the initial layer and ensure the nozzle isn't too far from the bed—it should gently "squish" the plastic onto the surface.
-
Problem: What Are These Spiderwebs? (Stringing):
- Quick Fix: This is caused by plastic oozing as the nozzle travels. In your slicer software, find the "Retraction" settings. Try increasing the retraction distance by 0.5mm or the retraction speed by 5mm/s to see if it improves.
- Next Step: Make sure your filament is dry. Moist filament can cause stringing. If it's been out for a while, consider drying it in a filament dryer.
Feeling these early growing pains is a sign you're on the right track. You're joining a massive global movement, with the 3D printing market projected to hit an incredible USD 64.79 billion by 2030. You can see the data on these 3D printing market findings to get a sense of how big this is getting. Every problem you solve is a skill you've earned, putting you at the forefront of a technology that is truly changing our world.
At Griseo Interior, we pour that same spirit of modern making into timeless Italian design, creating each piece just for you. Come discover our collection of minimalist home décor and bring purposeful beauty into your home.
